COVID-19 Drug Development Status
Pharma Intelligence Latest daily statics
- 456 R&D pipeline drugs
- 2451 clinical trials
The gap between experimentation and industry progress
- These trials are largely sponsored by academia and government, and promoted by reusing drugs.
- Few industry projects are at the clinical stage.
Drug pipeline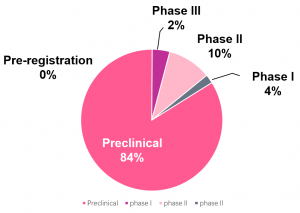
Treatment Paradigm
Biopharmaceutical companies are developing multiple therapies at different speeds.
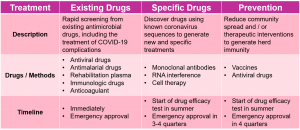
Innovative R&D
In the near future, biopharmaceutical companies will provide more effective treatments that are suitable for large stockpiles and for preventive use.
The first new antiviral drugs entered clinical trials this summer.
- The drugs are competing with a large number of existing tests.
- They still require community communication for verification that will continue throughout 2020.
- It can also be positioned as a preventive drug, providing a bridge for the wide supply of vaccines.
Vaccine is the most ideal and scalable treatment plan, attracting industry to work together for this.
- The tight timetable condenses various research and development work.
- Huge R&D scale is to compensate for expected risks.
- About 170 projects cover 10 different vaccine technologies.
- The scale of production continues to expand to meet market demand.
COVID-19 Drug Development Partnership
The industry is uniting and working together to tackle COVID-19. Biopharmaceutical companies not only cooperate with each other, but also cooperate with government agencies, non-governmental organizations, and academia to share resources and expertise.
Alliance
- National Institute of Health: Accelerating COVID-19 treatment interventions and vaccine development.
- Bill Gates Foundation: Accelerator for COVID-19 Therapy.
- World Health Organization: Access to COVID-19 tools (ACT) accelerator.
Partnership
- Increasing number of R&D alliances and licensing agreements.
- Institutions like BARDA and CEPI also funded early research.
Clinical Interruptions
Community isolation and point-of-care disruptions can affect clinical operations.
Almost all biopharmaceutical and CRO companies have indicated that they will discontinue ongoing and planned clinical trials.
- Except for key areas of focus, new sites and patient recruitment are generally suspended.
- Existing trials are still going on and will be modified if necessary to ensure continuity.
Although indicators now point to stabilization and recovery, the scale of the interrupted tests is difficult to quantify.
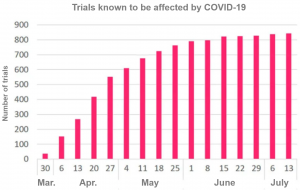
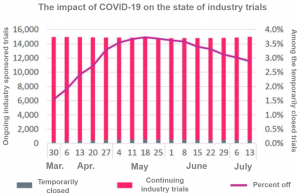
Focus on Trials Affected by COVID-19
There have been experimental disruptions in all areas of drug development.
Trialtrove notes that research has been subject to varying degrees of interference and that many studies have been able to continue, however, this influence is pervasive in many areas of biopharmaceuticals.
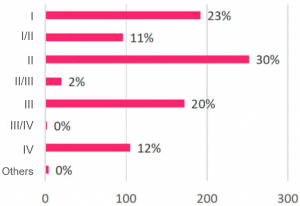
- Clinical stages – early, middle and critical stages are affected.
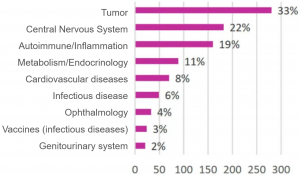
- Treatment area – relative ranking is consistent with all ongoing trials.
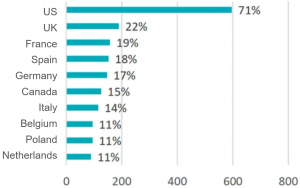
- Test sites – biased towards the US and the EU-5, and China and Japan were not listed the top 10.
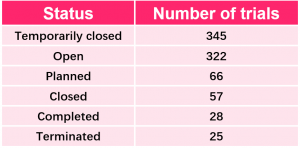
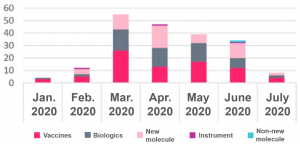
Cross-sectional View of A Trial Disturbed by COVID-19
An Industry Response to Mitigate Clinical Disruption
How can biopharmaceutical companies maintain r&d momentum during the COVID-19 pandemic?
Biopharmaceutical companies must maintain as much continuity as possible to improve patient outcomes.
Interrupting trials delays access to new treatments, causing collateral damage, but also avoiding the possible increased risk of coronavirus exposure.
Move to Decentralized Virtual Trials
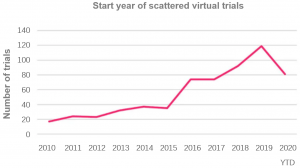
Scientists are accelerating clinical trial innovation.
Decentralized virtual trials offer the possibility of continuing clinical research by transferring medical points.
Industry acceptance rates are still low, but COVID-19 has sparked growing industry interest and concern.
Digital and virtual innovations in clinical trials include:
- Online consent forms, tied to electronic health records.
- Decentralized care, including mobile clinics.
- Patients report results and wearables.
- Remote monitoring of telemedicine for patients.
- Real-time tracking of clinical trials.
Broad benefits include cost, time, convenience, diversity, and resistance to COVID-19 destruction.
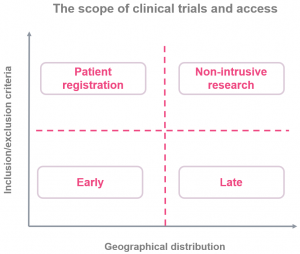
Diversity of Clinical Studies
Expand trial scope and inclusion to speed up research.
Trial sponsors should also seek to further expand the scope of trials to accelerate the pace of clinical research.
- Wider geographic distribution: countries with low COVID-19 exposure, recovering/resilient.
- Looser inclusion criteria: comorbidity, age.
- Patient demographics: for minority groups.
This will accelerate the pace of clinical research and improve its quality/applicability in different regions of the world.
Trade-offs are made in terms of sample homogeneity of introduced variables, which may require a larger sample size to achieve equivalent statistical efficacy.
Rationalization exclusion criteria. At the extreme, regulators need to receive real evidence.